Ergonomy
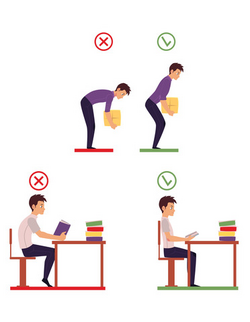
Ergonomy is about fitting the work to match your body and not the other way around. This should be considered at your office desk where table, chair and computer accessoires must be fitted to the individual user. But also related to the tasks involving moving items (by lifting, pushing or pulling).
Don't forget to take a break!
Charlotte Rasmussen has participated in a workshop regarding good office ergonomy.
How to avoid injuries
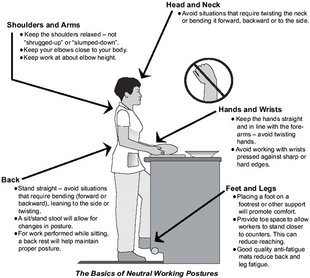
- Keep your body fit, make sure your muscles and joints are strong.
- Avoid heavy lifting (i.e. by placing objects on shelves and in cupboards according to their weight and how often you use them).
- Use appropriate tools (i.e. use a cart that you can pull or push, instead of carrying).
- Avoid monotonous, repetitive work: Try to vary your positions during the day.
- Distribute the load (walk twice with a bunch of parcels instead of once).
- Take a break.
Office
It is important to design your work space from day 1. Start with the chair, then adjust the table and lastly fit other equipment (computer/monitor, microscope, desk lamp etc.).
- A good chair will provide you with the ability to change posture often.
- All personal desks must be adjustable. Elevate the table once in a while to change your position.
- Consider a foot rest.
Adjusting a chair:
- Sit on the chair (make sure your entire foot is resting comfortably on the floor during the fitting).
- Adjust the height of the seat (activate the tilting function if you can).
- Adjust the depth of the seat (you should be able to fit a hand between the back of your knee and the front of the chair).
- The back rest must support your lower back: Use your hand to locate the place with the deepest bend on your back. Then adjust the back rest to support this bend when your back is in a straight position.
- If applicable: Adjust the weight resistance.
Nb: A simple thing as changing your shoes may require that you need to re-adjust your chair to achieve a comfortable position.
Adjusting the desk:
When sitting or standing at the table, the table top must be able to support your forearms comfortably, without you leaning forward or pushing your arms upwards. When working, place your body close to the edge of the tabletop (preferably in the center of the arc, if there is one).
- Stand or sit at the desk: You should apply equal weight to both your legs (relax in your knees, your foot soles should make perfect contact with the floor).
- Adjust the height of the table (your lower arms should be supported by the tabletop).
Laboratory
Microscopes:
Neck, shoulders and back are the most exposed body parts: Make sure to change position often and adapt the microscope to a pleasant height. You may want to elevate the microscope on a stand. Your arms must be able to rest on the table top. Preferably use a microscope with an adjustable tube to avoid bending your neck at an uncomfortable angle.
Fume hoods:
If you stand regularly at the fume hood, get a soft floor mat that will relieve the strain on your feet, legs and back. Alternatively, explore if a different type of chair would fit you and the situation better (saddle chair or chair with a foot rest).